1db compression point test|what is 1db compression point : online sales The 1 dB compression point (P1dB) is the output power level at which the gain decreases 1 dB from its constant value. Once an amplifier reaches its P1dB it goes into compression and becomes a non-linear device, producing . web28 de jan. de 2022 · No primeiro dia de atendimento, o drive montado pela Prefeitura do Natal, na Arena das Dunas, realizou 1.277 coletas do teste rápido tipo swab .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Pack Antigremista / Bialaurt . Pack da antigremista / bialaurt mais de 30 mídias vem pv Archived post. New comments cannot be posted and votes .
For a linear device, output power is merely a fixed fraction of the input power. This includes most passive devices such as connectors, cable, waveguides, etc. Nonlinear devices exhibit complex behavior when input power is compared to output power. However, most nonlinear devicestend to become lossier with . See moreAs we said, most components tend to lose gain (or have increasing loss) as power levels are increased. An example of a component that breaks this rule is a voltage-variable attenuator, at least in its high-loss state. If your attenuator needs to provide eight dB, it is . See moreIf you want your system to "act linearly", you need to stay well below the one dB compression point. This can lead to serious inefficiency, for example, you might need to use a 10 watt amp backed off to one watt output power. If your system is required to . See more
wagner moisture meter l622
The "classic" way to display power transfer characteristics is to plot the pairs of input and output power data, from linear to nonlinear operation of the device. The data is plotted, here . See more The 1 dB compression point (P1dB) is the output power level at which the gain decreases 1 dB from its constant value. Once an amplifier reaches its P1dB it goes into compression and becomes a non-linear device, producing .
There are two key measurements in determining power amplifier quality, efficiency, and linearity: the third-order intercept (abbreviated TOI or IP3) point and the 1-dB compression (P1dB) point. Understanding P1dB, or the 1dB compression point, is crucial for engineers and designers working with RF (Radio Frequency) and microwave amplifiers, as it provides a clear indication of an amplifier's linearity and . In this video Gregory presents the concept behind the 1db Compression Point of an RF amplifier. The measure is performed using a Signal Generator and a Spect.
1dB P m the 1dB compression point of the m-th component, and sat P in is the amount of receiver input power required to cause that particular component to saturate. Now, let’s look at .The 1-dB compression point (1-dB CP) is an important design parameter. The 1-dB CP is defined as the point at which the linear output power and the output power of the amplifier or nonlinear .
The 1 dB compression point of an amplifier is the input power required to reduce the gain (transducer power gain, GT) to 1 dB below its small-signal value. This value can be measured .1dB compression point measurement. It is also called as gain compression point; it is the output power till DUT works well and does not go into saturation condition. Keep varying the input power and measure the output power. From . At one input point, just below an input level of -5 dBm in Fig. 3, the actual output falls exactly 1 dB below the expected ideal output. This point is called the 1-dB compression point, abbreviated P1dB, and it serves as a .1dB compression point measurement . It is also called as gain compression point; it is the output power till DUT works well and does not go into saturation condition. Keep varying the input power and measure the output power. From .
SECOND AND THIRD-ORDER INTERCEPT POINTS (IP2, IP3), 1-dB COMPRESSION POINT . Third-order IMD products are especially troublesome in multi-channel communications systems where the channel separation is constant across the frequency band. Third-order IMD products can mask out small signals in the presence of larger ones. Compression is a measure of the linearity of a device. 1 dB compression is normally used as a standard for this measure. For an amplifier, it is defined as the output power at which the gain decreases by 1 dB from the .
The most common measurement of amplifier compression is the 1-dB compression point. This is defined as the input power (or sometimes the output power) which results in a 1-dB decrease in amplifier gain (relative to the amplifier's small-signal gain). . use a preamplifier to boost the power level prior to the amplifier under test. If using a .
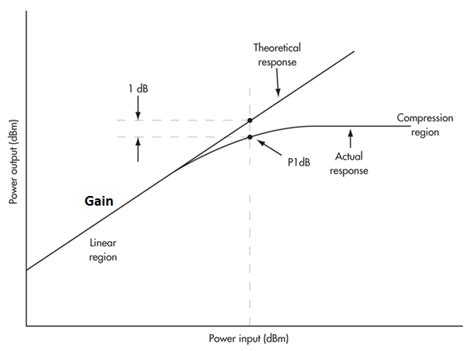
"The 1 dB Compression Point test is performed with the same CW setup used during the previous cross polarization test. This test establishes the point at which the Satellite Router’s transmit power saturates the BUC. 1. While still in iSite Cross Polarization dialog box and the Network Operator is watching the CW, increase the transmit power . The 1-dB compression point for an amplifier, for example, is where the linearity of the component begins to degrade. Under linear conditions, a 1-dB rise in input power will result in a 1-dB increase in output power. . Intercept points can be determined as a function of harmonics, using single-tone test signals , or by intermodulation .To quantify the linear operating range of the amplifier, we define the 1-dB Compression Point as the power level for which the output power has decreased by 1 dB from the ideal linear .
1dB gain compression point test method is more flexible, through the vector network analyzer automatic test, you can automatically test the compression point when the 1D / 2D scan; can also be based on the signal source and spectrum meter or even power meter for manual testing, which will be the following to highlight the method. This point is called the 1-dB compression point, abbreviated P1dB, and it serves as a useful figure of merit for RF devices. It can be referenced to either the input (IP1dB) or the output (OP1dB). Figure 3. The actual response falls exactly 1 dB below the ideal response at the 1 dB compression point. Figure 4.Graphically (Figure 13), it is the point where the actual input-output response curve deviates (i.e., drops) by 1dB from the linear asymptote. Figure 13. Graphical view of a -1dB compression point. The −1dB compression point can also be seen as the point where the actual curve crosses the linear dropped by 1dB asymptote.
Compression point is a measure of linearity of a device. It is always defined at a specified value of which can be referenced to the input or the output power that is present at that device. For instance the 1dB compression point of an amplifier defines the output level at which the amplifier’s gain is 1dB less than the small signal gain, or . In order to determine the 1dB compression point (P-1dB) of the PA, the input voltage amplitude of the PA is increased until a 1dB drop in the linear gain of the PA is observed.11/1/2006 Receiver Compression Point 4/14 Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS Here the value G m represents the gain of the m-th component, 1dB P m the 1dB compression point of the m-th component, and sat P in is the amount of receiver input power required to cause that particular component to saturate. Now, let’s look at each component, and determine its
compression point and IP3 on low cost tests, without used instruments and in short time, BIST circuit is presented [1]. Shorter test times, being able to switch on any time during
1dB Compression Point . As you see in the plot show below, to some point the ideal operation curve and real operation curve of an amplifier is almost identical (i.e, within linear operation region) but from a certain point the real output .There is one (and only one!) point on the mixer curve that satisfies the equation: (dBm) (dBm) Conversion Loss(dB) 1 dB IF RF PP=− − This point is the 1 dB compression point of the mixer! * At the 1 dB compression point, the conversion loss appears to be 1 dB greater than its normal (i.e., low power) value.
At one input point, just below an input level of -5 dBm in Fig. 3, the actual output falls exactly 1 dB below the expected ideal output. This point is called the 1-dB compression point, abbreviated P1dB, and it serves as a . Episode 908Measuring the 1dB compression power level of an amplifierBe a Patron: https://www.patreon.com/imsaiguyP1dB or 1dB compression point is the part of the curve where, 2dB change in the input power fed to the amplifier(RF circuit) results into 1 dB change in the output power. The input and output powers are called as P1B in and P1dB out respectively. In reality, Intercept point is usually about 10 dB higher value compare to P1dB (1dB compression . Video to illustrate the evaluation of the 1-dB gain compression point for an RF amplifier.
degrade before the signal peak hits the P1dB compression point. The EVM for the GaAS device rises to nearly 0.4% well before the signal peak hits the 0.1dB point, whereas the EVM for the UltraCMOS device stays below the measurement noise floor. This could be criticalOutput power is defined in terms of the 1 dB compression point (P1dB) and P3dB, which is practically very close to the saturated output power capability of the amplifier. . Operating the amplifier at one of the test frequencies points, the input power to the PA will be increased until the output CCDF at 0.01% probability reaches 9.8dB minus .1-dB compression points, but there is no reliable method for predicting one value from the others. Two receivers with identical 1-dB compression points may have third-order intercept points which differ from each other by as much as 20 dB, and vice versa. For this reason, the 1-dB compression point is a useful specification to supplement
In telecommunications, a third-order intercept point (IP 3 or TOI) is a specific figure of merit associated with the more general third-order intermodulation distortion (IMD3), which is a measure for weakly nonlinear systems and devices, for example receivers, linear amplifiers and mixers.It is based on the idea that the device nonlinearity can be modeled using a low-order .The 1 dB compression point (P1dB) is the output power level at which the gain decreases 1 dB from its constant value. i.e. OP1dB (dBm) = IP1dB (dBm) + Small Signal Gain (dB) - 1 dB . Importance of Test and Measurement Instruments. December 28, 2018. Most Recent 3/recent/post-list Random Posts 3/random/post-list Who We Are More about us .1 dB compression point defines the output level at which the amplifier's gain is 1 dB less than the small signal gain, or is compressed by 1 dB (P1dB). Out. p ut Power . Saturated Output Power (P SAT) ∆= 1dB. P. 1dB (Output Power at 1 dB Compression) Input Power . NOTE: Most amplifiers start to compress approximately 5 to 10 dB below P1dB.1 dB compression point (P1dB) on a graph of the transfer function (in German). An ideal amplifier will produce a straight line (German: ideale Kennlinie).A real-world amplifier has an output power limit and will therefore exhibit gain compression (German: reale Kennlinie). The compression point is a metric describing an aspect of electronic amplifiers. .
what is p1db
web25 de jun. de 2020 · Disfruta de la canción de vallenato Amarte Más No Pude, interpretada por Diomedes Díaz. La letra expresa el dolor de perder el amor de su vida y no poder olvidarla.
1db compression point test|what is 1db compression point